LDO Full From is Low-Dropout
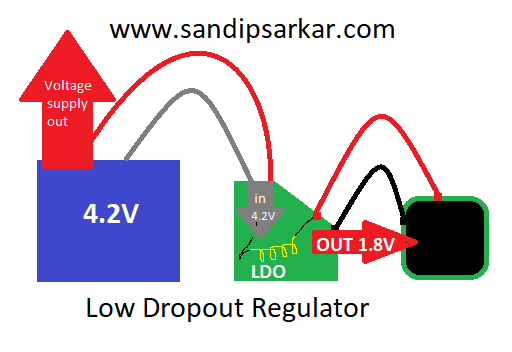
LDO stands for “low dropout”, which is a type of voltage regulator commonly used in electronic circuits.
LDO Full Details
A low dropout regulator (LDO) is a type of voltage regulator that is commonly used in electronic circuits to provide a stable and regulated output voltage. The primary function of an LDO is to regulate the voltage of an input voltage source to a lower, constant output voltage, even if the input voltage varies over a certain range.
The main advantage of an LDO over other types of voltage regulators is that it can regulate the output voltage with a very small voltage drop between the input and output, typically less than 0.5 volts. This means that an LDO can regulate the output voltage very close to the input voltage, which is particularly useful when the input voltage is close to the required output voltage.
LDOs are commonly used in many types of electronic devices, including mobile phones, laptops, and other portable electronic devices. They are also used in power management circuits in many other types of electronic systems, such as industrial control systems, automotive systems, and aerospace systems.
Type of LDO
There are several types of LDOs available, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Here are a few examples:
- Standard LDOs: These are the most commonly used LDOs and are designed to provide a fixed output voltage with a low dropout voltage. They typically have low output noise and high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio), making them suitable for many applications.
- Low Noise LDOs: These LDOs are designed to provide a very low output noise, making them suitable for noise-sensitive applications such as audio circuits, RF circuits, and sensitive instrumentation.
- High PSRR LDOs: These LDOs are designed to have a high power supply rejection ratio, meaning that they can reject noise and ripple on the input power supply. They are suitable for use in applications where the input voltage may be noisy or unstable.
- Adjustable LDOs: These LDOs allow the output voltage to be adjusted by the user, making them suitable for applications where a variable output voltage is required.
- LDOs with Power Good or Reset Function: These LDOs have a built-in power good or reset function, which monitors the output voltage and generates an output signal when the voltage reaches a certain level. This can be useful in applications where a clean and stable power supply is critical.
Standard LDO
Standard LDOs are the most commonly used type of low dropout regulators. They are designed to provide a fixed output voltage with a low dropout voltage. The dropout voltage is the minimum voltage difference between the input voltage and the regulated output voltage required for the LDO to maintain regulation.
Standard LDOs typically have a low output noise and high power supply rejection ratio (PSRR), making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are often used to provide a stable and regulated voltage to microcontrollers, sensors, and other digital circuits that require a precise and stable power supply.
Standard LDOs can be found in various packages, including surface-mount and through-hole packages, and are available in both positive and negative output voltage configurations. They also have different maximum and minimum input and output voltage ratings, output current capabilities, and other specifications, which should be carefully considered when selecting an LDO for a particular application.
Overall, standard LDOs are a reliable and cost-effective solution for many low-power and low-voltage applications that require a stable and regulated power supply.
Low Noise LDOs are a type of low dropout regulator that are designed to provide a very low output noise level. They are particularly suited for applications that are sensitive to electrical noise, such as audio circuits, RF circuits, and sensitive instrumentation.
The output noise of an LDO is a measure of the unwanted variations in the output voltage that can result from internal circuit noise or external interference. Low Noise LDOs are designed to minimize these variations by incorporating additional circuitry, such as noise-reducing filters, to reduce the noise levels.
Low Noise LDO
Low Noise LDOs are typically used in applications where a clean and stable power supply is critical. For example, they can be used to provide a low-noise power supply for analog-to-digital converters, or to power sensitive sensors that require a low-noise power source.
When selecting a Low Noise LDO, it is important to consider the noise specification, as well as other important factors such as input and output voltage range, output current capability, and thermal performance. It is also important to consider the overall system noise budget to ensure that the LDO’s output noise level is compatible with the requirements of the system.
High PSRR LDO
High PSRR (Power Supply Rejection Ratio) LDOs are a type of voltage regulator that are designed to reject noise and ripple on the input power supply. PSRR is a measure of how well the LDO is able to reject variations in the input voltage and provide a stable output voltage.
High PSRR LDOs are particularly useful in applications where the input voltage may be noisy or unstable, such as in automotive or industrial environments. They are also useful in applications where a high level of noise immunity is required, such as in data acquisition systems or precision measurement equipment.
High PSRR LDOs typically have additional filtering and decoupling circuitry to help suppress input noise and ripple. They are designed to provide a stable output voltage even in the presence of significant variations in the input voltage.
When selecting a High PSRR LDO, it is important to consider the PSRR specification, as well as other important factors such as input and output voltage range, output current capability, and thermal performance. It is also important to ensure that the LDO’s PSRR is compatible with the requirements of the system, and that the overall noise budget of the system is taken into account.
Overall, High PSRR LDOs are a reliable and cost-effective solution for many applications that require a stable and regulated power supply in noisy environments.
Adjustable LDO
An adjustable LDO is a type of low dropout regulator that allows the user to adjust the output voltage to a specific value within a specified range. This flexibility makes adjustable LDOs useful in applications where a fixed output voltage is not suitable, or where the output voltage needs to be varied for different operating conditions.
Adjustable LDOs typically have an external resistor network that is used to set the output voltage. By adjusting the value of the external resistors, the output voltage can be set to the desired value. The range of the adjustable output voltage depends on the specific LDO, but it is typically a few volts.
Adjustable LDOs are commonly used in applications such as battery-powered devices, where the input voltage may vary depending on the state of the battery. They are also useful in applications where the output voltage needs to be varied for different operating conditions, such as in LED lighting applications or motor control circuits.
When selecting an adjustable LDO, it is important to consider the output voltage range, the maximum output current capability, the dropout voltage, and the input voltage range. It is also important to ensure that the external resistor network is correctly designed to provide the desired output voltage range.
Overall, adjustable LDOs are a flexible and cost-effective solution for applications that require a regulated output voltage that can be adjusted to different values within a specific range.
LDOs with Power Good or Reset Function
An LDO with a Power Good or Reset function is a type of low dropout regulator that includes a built-in circuit to monitor the output voltage and generate an output signal when the voltage reaches a certain level. This feature can be useful in applications where a clean and stable power supply is critical, or where a reset signal is needed to ensure proper system operation.
The Power Good function is typically used to monitor the output voltage of the LDO and provide an indication when the voltage is within a specific range. This can be useful in applications where the output voltage must be within a certain range for proper system operation. The Power Good signal can be used to enable downstream circuitry or to trigger an alarm or other alert if the output voltage is out of range.
The Reset function is typically used to ensure proper system operation by providing a reset signal when the output voltage is stable and within a specific range. This can be useful in applications where a clean and stable power supply is critical for proper system operation. The Reset signal can be used to reset microcontrollers, digital circuits, or other system components when the power is turned on, or in response to certain events.
When selecting an LDO with a Power Good or Reset function, it is important to consider the specific voltage range and timing requirements of the application. It is also important to ensure that the Power Good or Reset function is compatible with the other system components and that any necessary interface circuitry is correctly designed.
Overall, an LDO with a Power Good or Reset function can provide added functionality and convenience for applications that require a clean and stable power supply or a reset signal for proper system operation.
How to check LDO
To check if an LDO is working properly, you can follow these steps:
- Check the input voltage: Ensure that the input voltage is within the LDO’s specified operating range. The input voltage should be within the LDO’s maximum and minimum input voltage ratings. If the input voltage is too high or too low, the LDO may not regulate properly.
- Measure the output voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the LDO’s output voltage. The output voltage should be within the LDO’s specified output voltage range. If the output voltage is too high or too low, the LDO may not be regulating properly.
- Check the dropout voltage: Measure the voltage across the input and output pins of the LDO. The voltage difference between the input and output pins should be within the LDO’s specified dropout voltage range. If the dropout voltage is too high, the LDO may not be able to regulate the output voltage properly.
- Check for thermal issues: Check the LDO’s temperature to ensure that it is not overheating. An overheating LDO may not regulate properly and can cause other problems in the circuit.
- Check for load regulation: Apply a load to the LDO and measure the output voltage. The output voltage should remain within the LDO’s specified range even with changes in the load. If the output voltage varies significantly with changes in the load, the LDO may not be regulating properly.